Stream이란?
데이터의 흐름에서 원하는 값을 가공하여 원하는 값을 리턴하는 역할을 수행
스트림은 컬렉션(배열)의 저장 요소를 하나씩 참조해서 람다식으로 처리할 수 있도록 해주는 반복자이다
내부 반복자를 사용하므로 병렬처리가 쉽다
스트림 생성
.stream()
- 배열 스트림
- Stream.of("a", "b", "c")
- IntStream.of(1,2,3)
- Arrays.stream(arr)
- 컬렉션 스트림
Stream.builder()
- Builder를 사용하면 스트림에 직접적으로 값을 넣을 수 있음
- .build메서드로 스트림을 리턴함
Stream<String> builderStream =
Stream.<String>builder()
.add("A").add("B").add("V")
.build(); // [A, B, C]중간 연산
매핑, 필터링, 정렬을 수행
distinct()
중복을 제거
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "A", "A", "C");
names.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println); // [A, B, C]
}
}filter
특정 조건에 해당하는 객체만 작업
조건문 if와 동일
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "A", "A", "C");
names.stream()
.distinct() // 중복 제거
.filter(name -> name.equals("C")) // 이산이라는 이름을 가진 이름만 리스트에 남겨 둠.
.forEach(System.out::println); // [C]
}
}Mapping
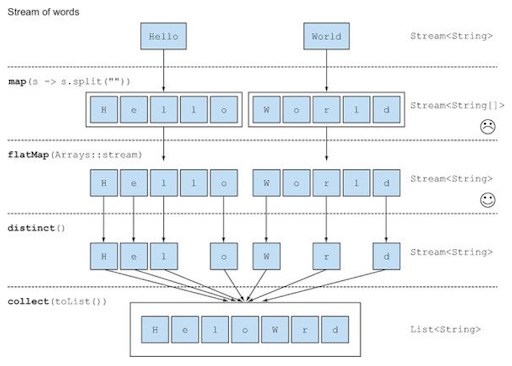
flathMap()
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world");
long res = inputList.stream()
.flatMap(data -> Arrays.stream(data.split("")))
.count();
System.out.println(res); // 10
}
}map()
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world");
long res = inputList.stream()
.map(s -> Arrays.stream(s.split("")))
.count();
System.out.println(res); // 2
}
}
mapToInt()
int값의 배열?로 변환
boxed()
레퍼런스 타입으로 변환 (박싱)
sorted()
Comparable 구현 방법에 따라 정렬
sorted(Comparator<T>)
sorted( (o1, o2) -> a - b)
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Member> memberList = Arrays.asList(
new Member("A", 22),
new Member("B", 23),
new Member("C", 20)
);
memberList.stream()
.sorted((m1, m2) -> m1.getAge() - m2.getAge())
.forEach(m -> System.out.println(m.getName()));
}
}최종 연산
반복, 카운팅, 평균, 총합 등의 집계 처리 수행
findFirst, findAny
findFirst는 가장 처음의 객체
findAny는 아무 객체 중 하나를 꺼낸다
collect
- 스트림에서 꺼낸 데이터들을 다시 Collection화 할 때 사용한다
- collect(Collectors.toList())
- collect(Collectors.toSet())
- 그룹화
- collect(Collectors.groupingBy(객체::변수)) (Map 변수로 저장됨)
- 값 가져오기
average()
요소 평균, double타입
count()
요소 갯수, long타입
sum()
요소 총합, int, long, double 타입
getAsDouble()
'CS > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 배열 제어하기 예제 - 스트림 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList 효율성 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 메서드 - 람다식 (compare) (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 문자열 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| Primitive Type & Reference Type (0) | 2024.07.30 |
Stream이란?
데이터의 흐름에서 원하는 값을 가공하여 원하는 값을 리턴하는 역할을 수행
스트림은 컬렉션(배열)의 저장 요소를 하나씩 참조해서 람다식으로 처리할 수 있도록 해주는 반복자이다
내부 반복자를 사용하므로 병렬처리가 쉽다

스트림 생성
.stream()
- 배열 스트림
- Stream.of("a", "b", "c")
- IntStream.of(1,2,3)
- Arrays.stream(arr)
- 컬렉션 스트림
Stream.builder()
- Builder를 사용하면 스트림에 직접적으로 값을 넣을 수 있음
- .build메서드로 스트림을 리턴함
Stream<String> builderStream =
Stream.<String>builder()
.add("A").add("B").add("V")
.build(); // [A, B, C]중간 연산
매핑, 필터링, 정렬을 수행
distinct()
중복을 제거
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "A", "A", "C");
names.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println); // [A, B, C]
}
}filter
특정 조건에 해당하는 객체만 작업
조건문 if와 동일
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "A", "A", "C");
names.stream()
.distinct() // 중복 제거
.filter(name -> name.equals("C")) // 이산이라는 이름을 가진 이름만 리스트에 남겨 둠.
.forEach(System.out::println); // [C]
}
}Mapping
flathMap()
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world");
long res = inputList.stream()
.flatMap(data -> Arrays.stream(data.split("")))
.count();
System.out.println(res); // 10
}
}map()
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> inputList = Arrays.asList("Hello", "world");
long res = inputList.stream()
.map(s -> Arrays.stream(s.split("")))
.count();
System.out.println(res); // 2
}
}
mapToInt()
int값의 배열?로 변환
boxed()
레퍼런스 타입으로 변환 (박싱)
sorted()
Comparable 구현 방법에 따라 정렬
sorted(Comparator<T>)
sorted( (o1, o2) -> a - b)
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Member> memberList = Arrays.asList(
new Member("A", 22),
new Member("B", 23),
new Member("C", 20)
);
memberList.stream()
.sorted((m1, m2) -> m1.getAge() - m2.getAge())
.forEach(m -> System.out.println(m.getName()));
}
}최종 연산
반복, 카운팅, 평균, 총합 등의 집계 처리 수행
findFirst, findAny
findFirst는 가장 처음의 객체
findAny는 아무 객체 중 하나를 꺼낸다
collect
- 스트림에서 꺼낸 데이터들을 다시 Collection화 할 때 사용한다
- collect(Collectors.toList())
- collect(Collectors.toSet())
- 그룹화
- collect(Collectors.groupingBy(객체::변수)) (Map 변수로 저장됨)
- 값 가져오기
average()
요소 평균, double타입
count()
요소 갯수, long타입
sum()
요소 총합, int, long, double 타입
getAsDouble()
'CS > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 배열 제어하기 예제 - 스트림 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList 효율성 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 메서드 - 람다식 (compare) (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 문자열 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| Primitive Type & Reference Type (0) | 2024.07.30 |
